Electric Field Due To Infinite Line Charge Derivation

For a line charge a surface charge and a volume charge the summation in the definition of an electric field discussed previously becomes an integral and qi is replaced by dq λdl σda or ρdv respectively.
Electric field due to infinite line charge derivation. Field from infinite plate part 1. Point charges e p 1 4πϵ0 line λdl r2 ˆr. Electric potential of finite line charge. Electric field of line charge the electric field of an infinite line charge with a uniform linear charge density can be obtained by a using gauss law.
Finding the electric field of an infinite line of charge using gauss law. Written by willy mcallister. This is the currently selected item. Electric field due to an infinite line of charge or uniformity charged long wire or thin wire an infinite line of charge may be a uniformly charged wire of infinite length or a rod of negligible radius.
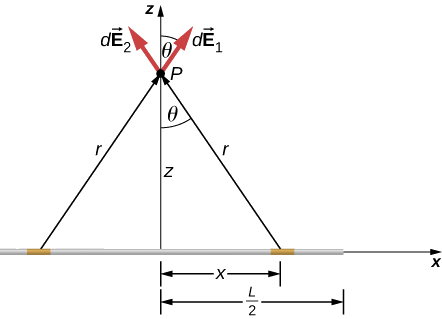
The integral required to obtain the field expression is. E p 1 4πϵ0 n i 1 qi r2 ˆr. Electric field surrounding a uniformly charged infinite line. We can take advantage of the cylindrical symmetry of this situation.
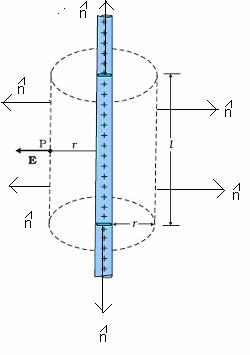
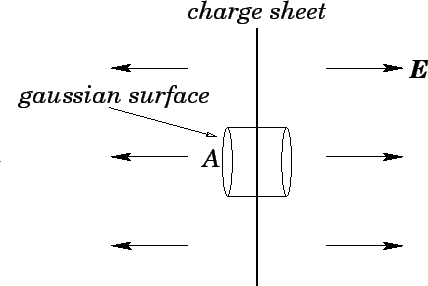
Electric field of an infinite line of charge find the electric field a distance above the midpoint of an infinite line of charge that carries a uniform line charge density. Use gauss law to determine the electric field intensity due to an infinite line of charge along the z axis having charge density rho l units of c m as shown in figure pageindex 1. Considering a gaussian surfacein the form of a cylinder at radius r the electric field has the same magnitude at every point of the cylinder and is directed outward. Electric field due to infinite wire gauss law application consider an infinitely long line of charge with the charge per unit length being λ.
The radial part of the field from a charge element is given by. While deriving the formula for electric field due to an infinitely long wire of uniform charge density using gauss s law we assume that this field has cylindrical symmetry and there is no component of field along the axis but how do we know that the field has cylindrical symmetry and there is no component of field along the axis why can t there be an axial component of field and what happens if we have a wire of finite length.